eBook
Building a Strong Data Foundation
for Vault CRM Migration
80% of reps struggle with bad data. A powerful CRM starts with a strong foundation. Get insights on how switching to connected data and software can enable a successful Vault CRM migration and long-term benefits.
The biopharma industry is transforming its tech stack by adopting Vault CRM, creating an opportunity to redefine the customer engagement ecosystem, including establishing a solid data foundation. While simultaneously migrating customer reference data and CRM might seem overwhelming, prioritizing a solid data foundation can make it easier for your company and enhance long-term success.
Get the data right, get CRM right
To take advantage of CRM's full potential, including capabilities such as Next Best Action (NBA), AI, or effective territory alignments and targeting, your CRM must rely on good data. Accurate and harmonized customer data is key to creating great crosschannel experiences and the accurate use of artificial intelligence. A connected data and software stack also facilitates and speeds up the Vault CRM migration, removing the need for complex and costly integrations.
Cost of migrating < cost of poor data
Perceived switching costs to a new technological solution could hinder change management. However, the hidden costs of having poor data far outnumber the switching costs. According to a Gartner study, poor data quality costs organizations nearly $13 million annually. Beyond financial losses, the negative impact on CRM adoption and field force efficiency can be equally detrimental to overall business performance.
What's the Cost of Poor-Quality, Fragmented Data?
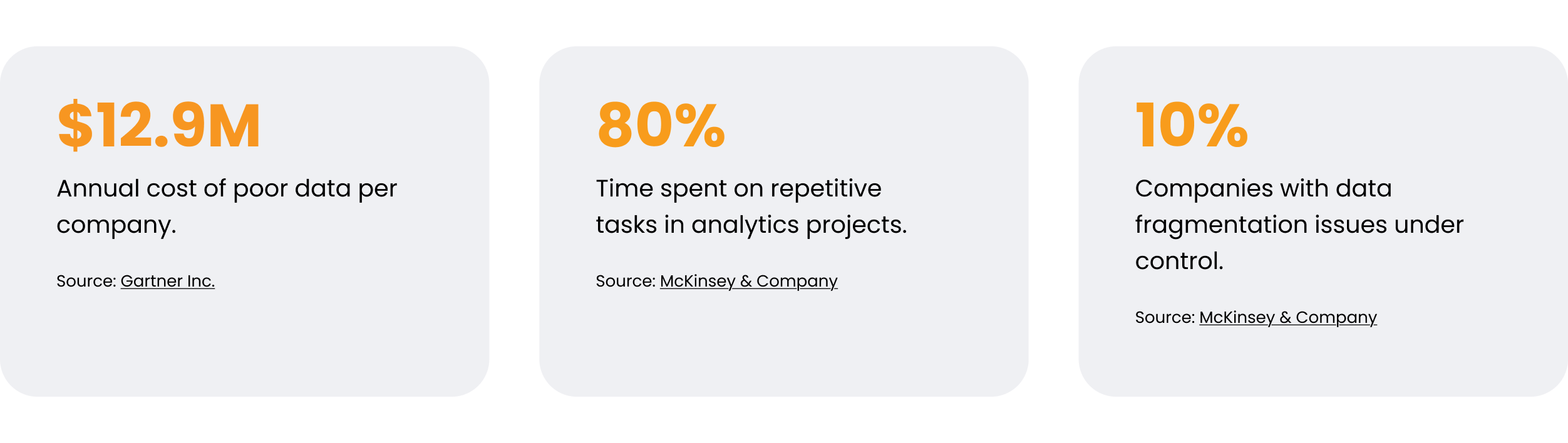
2McKinsey & Company
3McKinsey & Company
Making the Move
Companies often hesitate to switch providers due to concerns about potential business disruptions and productivity losses. Such transitions can involve intricate process redesigns, large-scale global projects, and extensive change management efforts across teams. About ninety-three percent of new Vault CRM customers have seamlessly transitioned to a connected data and software ecosystem through Veeva OpenData.
Veeva's goal is to minimize the operational impact through proactive change management while keeping the architecture the same, with flexible data mapping and formatting options.
Migration to Veeva OpenData will vary depending on your current MDM setup—or whether you use one. Veeva offers flexible options to support each scenario.
Scenario 1
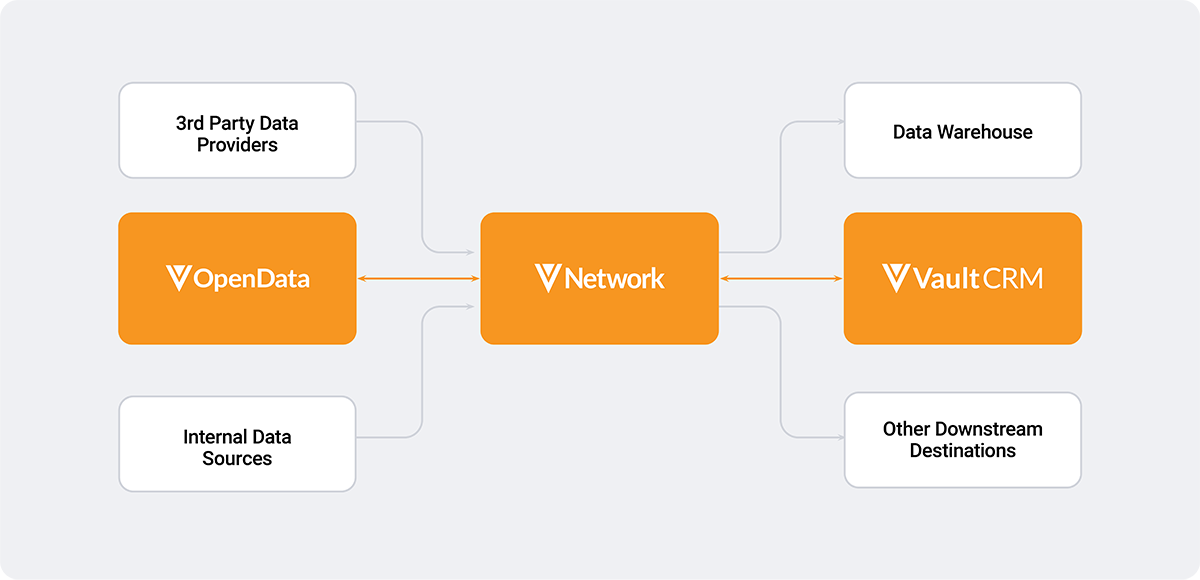
Veeva customer master data and software (Vault CRM, Veeva OpenData, and Veeva Network)
Veeva Network is a life-sciences-specific MDM preintegrated with Veeva OpenData and Vault CRM. This integration allows for a scalable and more straightforward data management solution, giving biopharma companies endless possibilities to manage diverse and complex data sources, including product, payer, and employee data.
As a result, moving to Veeva Network and Veeva OpenData before moving to Vault CRM can provide an automated migration experience once the integration is deployed.
This option requires minimal effort on your part, as Veeva manages both data and software migrations. Timelines can be flexible according to your requirements.
Scenario 2
Mixed customer data and software landscape (Vault CRM, Veeva OpenData, and third-party MDM)
Some biopharma companies prefer to keep their MDM in place. This option is possible through file delivery and the OpenData API, which provides programmatic access to Veeva OpenData information and functionality. In this option, migration to Veeva OpenData becomes a collaborative effort among the biopharma company, Veeva, and the third-party MDM integrator.
Leveraging the Common Data Architecture for Life SciencesTM (CDA) as a harmonization layer enables seamless integration of legacy data sources via standard files or the OpenData API, ensuring consistency and compatibility across systems.
Preparing for Migration
A clear understanding of the landscape is crucial for successful migrations. Here are key elements to define before migrating:
Migration scope
Identify which business areas, markets, or therapeutic areas to migrate. Focus the migration on accounts with the most interactions and those field reps use. This scope influences the overall timeline of your migration. Consider factors such as:
- Third-Party MDM: Using a third-party MDM increases complexity and requires custom integrations.
- Data volume: Larger datasets require more matching, validation, and testing time.
- Data modeling: More complex legacy systems, particularly those with custom fields, will take longer to map and integrate.
- Downstream systems: The more systems that consume reference data (e.g., BI tools, CRM, incentive compensation platforms), the longer the testing and validation.
Territory alignment structure
Decide whether you will use an Account-based or zip code-based alignment. Accurate territory alignment is crucial for sales force effectiveness, incentive compensation, and reporting.
Success metrics
Identify key metrics that will define a successful migration. Whether that means minimal disruption to the business during the migration process, a high match rate with your legacy data, or ensuring HCP data remains accurately attributed to the correct territories. Setting goals earlier ensures you can verify they’re considered at every migration step
Data sources
Ensure you know all the data sources included in the migration's scope. The third-party agreement (TPA) process can be long and complex, so identifying who owns the data will ensure timely delivery.
Stakeholders
Getting the right stakeholders onboard from the very beginning is crucial to ensure alignment of the project specifications. Involve the IT organization in technical requirements and the business stakeholders, such as commercial excellence leads, to ensure the field force is well aware of the upcoming transition.
A Five-Step Migration Process
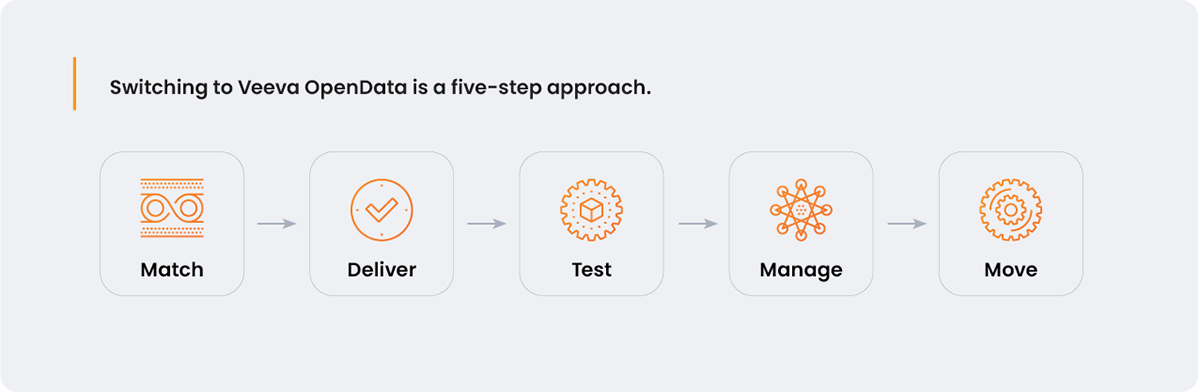
Step 1: Match

One of the core aspects of the migration process is data matching, which ensures that your legacy data matches with Veeva OpenData records. This step reveals the true scope of the work required on your data. However, the success of this process heavily depends on the quality of your data sources. Ensuring you have all the data you’d need is critical.
Having the minimum required fields for matching would be a beneficial first step, with unique identifiers playing a vital role in speeding up the process and improving accuracy, setting the foundation for a smooth transition to production.
The data matching process is simple:
- Download the data matcher tool provided by Veeva.
- Load your data and run the match.
- Analyze the results and non-matches.
Dealing with unmatched records
When you encounter unmatched records after generating the results, it’s essential to understand why they are not matching and create an action plan — whether to look into it through data stewardship or disregard it and raise a data change request (DCR) when it’s live.
If you own the unmatched record, you can keep it as customer-managed data within Veeva Network to distinguish it from Veeva OpenData records. Only some elements, such as name and address, can be kept if a third-party provider owns the data, which can be challenging to maintain.
Step 2: Deliver
If you are using Veeva Network as an MDM system, Veeva OpenData fields and Vault CRM fields will be mapped seamlessly, ensuring data consistency and accuracy across the system. This seamless integration allows for real-time DCR processing and HCP search and download.
Legacy data will be replaced with Veeva OpenData for matched records based on matching cross-references. New HCP and HCO data not in the initial database will be loaded, expanding the scope and value of the data within Vault CRM.
Step 3: Test

The next step is testing the data in your MDM and CRM, where user acceptance tests are done, as well as in other downstream systems.
These systems, such as business intelligence (BI) and analytics tools, incentive compensation platforms, territory alignment, and sampling solutions, rely on accurate reference data to function effectively. Testing involves working within a sandbox environment to ensure data flows smoothly into these downstream systems.
Step 4: Manage
Training for field teams and the trainers also occurs during this stage to ensure teams understand the change's impact on the business.
When the loading and testing are complete, you will notice changes in the data. The goal, however, is not to eliminate change but to minimize its impact. By moving to a connected data and software platform, you can expect data and services to improve.
Expected outcomes

Field rep support
Training for field teams and the trainers also occurs during this stage to ensure teams understand the change's impact on the business. By leveraging your field teams, they can help you minimize the impact:

Step 5: Move
The final step is transitioning to production. Switching to Veeva OpenData before Vault CRM can avoid downtime entirely. A typical migration, using a phased approach, takes 2–4 months. Each phase handles a portion of the data, ensuring that the transition is smooth and manageable.
Ensuring a Successful Migration
Switching to connected data and software might feel challenging, but with strategic planning, strong stakeholder alignment, and a clear, step-by-step approach in collaboration with the Veeva team, you can minimize risks and ensure a smooth transition.
Here are three considerations from one of the top 20 biopharma that effectively made the switch.

Tip 1: Track value and communicate it to end users
Evolving from best-of-breed data management toward utilizing Veeva OpenData as the single source of truth requires the application of change management principles. Provide stakeholders with proof points that capture the value of how data has improved outcomes — for example, reduced DCR processing times and faster time-to-insights.
Show field teams that you have considered their roles and goals by offering possibilities and use cases for what they can achieve using unified data. The competitive advantage goes far beyond reps being better prepared for HCP meetings. Operational teams benefit as well, receiving fewer tickets and duplicate tasks.

Tip 2: Consider all use cases and downstream impacts
When changing a master record, there are domino effects to consider. For example, a specialty might change from internal medicine to hematology-oncology, altering a subset of individual HCPs’ records. As a result, it’s essential to communicate the impacts at the macro and micro levels to stakeholders.
In addition, conduct analyses ahead of time and prepare for conversations with a wide range of stakeholders — some adept at data analysis and others not. Reference data has a specific purpose, though the use of it by various stakeholders can be very different and have wide-ranging effects. Investigate all potential use cases and develop a solution for everyone because later rule changes can disrupt operations.

Tip 3: Fix data fragmentation issues sooner rather than later
It’s common for commercial teams to become highly focused on operations, resulting in temporary fixes to data fragmentation and quality problems. The corrections often include adding new sources and vendors, new coding, and more data stewards.
By prioritizing the quality and accuracy of customer data during the migration process, you can ensure a more seamless transition and unlock the full potential of your customer engagement platform.
To learn more, read Optimizing Field Execution with Unified Customer Data.